💥Sycamore Partners is a B.E.A.S.T. Part I(b).💥
Speaking of feedback, one investor wrote us that the Twitterati — and PETITION to a lesser extent — had the Sycamore/Staples story all wrong. The dividend recapitalization doesn’t affect the retail story one way or another. That is because Sycamore did, in fact, separate the Staples business into multiple businesses, with the debt remaining at the Staples North American Delivery (“NAD”) entity. Staples U.S. Retail and Staples Canada Retail, as the other two units are now called, aren’t on the hook for the billions of dollars of debt. And, so, other than a bitchin’ new logo, Staples Retail isn’t really the story.* Once again, Sycamore is.
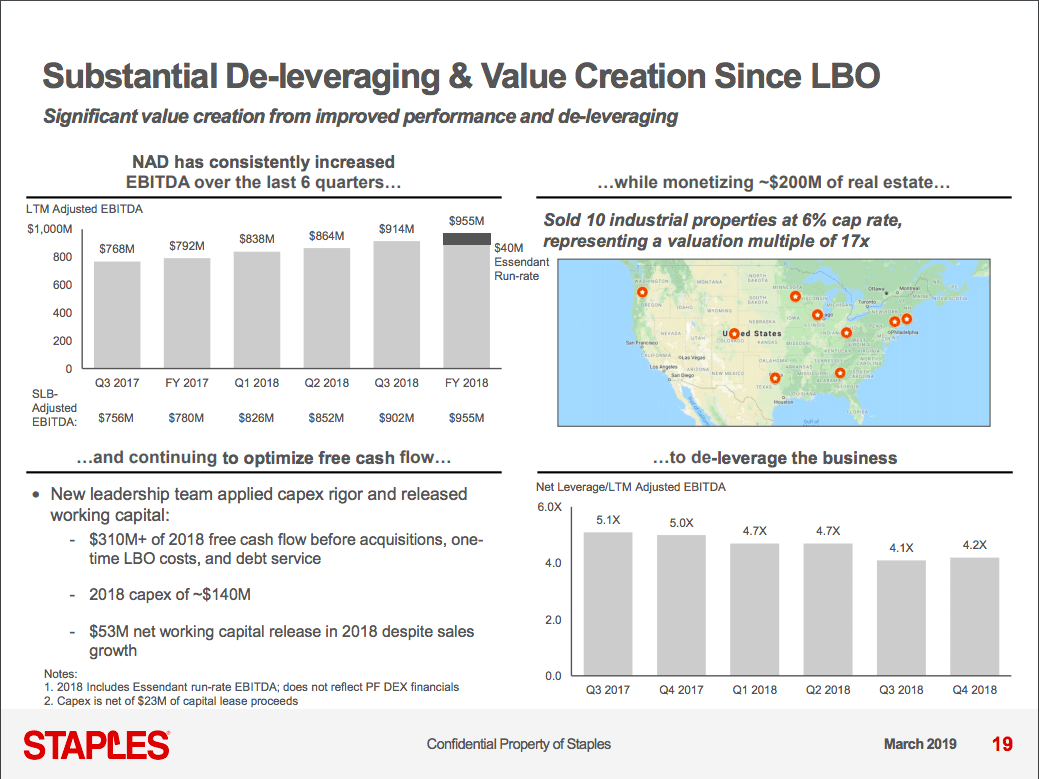
The Staples NAD lender presentation is an enlightening (and somewhat propagandist) look at the fast, furious and savage nature of the private equity model. In less than two years, Sycamore has (i) completed its intended business separation, (ii) improved EBITDA by $160mm “through stable top-line performance, expanded merchandise margins, and SG&A reductions, (iii) identified an additional $185mm of additional cost opportunities beyond 2019, (iv) bolted on some acquisitions, and (v) recruited 8 new members of the senior leadership team. Adjusted EBITDA is $1.2b (providing for certain acquisition-related addbacks). How the hell did Sycamore achieve all of this?
In part, by squeezing. The company has increased merchandise margins through “vendor negotiations.” Eat it vendors! Private equity is in the HOUSE!! The company reduced fiscal year ‘18 SG&A by over $100mm “through restructuring initiatives.” Eat it employees!! Private equity is in the HOUSE!! 900 of you can pack yo’ bags!! And hey you. Yeah you. Sales force employee #901 who thinks she’s safe. Well, newsflash: you’re not. Sycamore predicts another $19mm in sales force savings in 2019.
What about you, Mr. IT guy? That’s right:
Sycamore has another 70 full-time employees in the IT department slated for termination to the tune of $6mm in headcount savings. How? “Order management system consolidation.” Read: tech is replacing humans. Another $20mm of savings will come from robotics within Staples’ facilities. And yet another $10mm will come from outsourcing support from internal to low cost contractors (PETITION Note: short the US; long India). When talking heads say that PE strips out costs like a bawse, they’re not kidding. Is this dude on payroll?
NAD has fiercely competed to retain revenue and promote existing customer growth. Staples NAD now purportedly has ~2x as much revenue as Office Depot and ~3-4x more than Amazon Inc. ($AMZN). These guys sell a f*ck ton of office supplies, ink/toner and paper — about $5b worth. That’s insane. And they’re getting after the private label space, where the company has margins over 50%.
To put a finer point on this, look at this slide:
These guys aren’t messing around. These guys did their thing and now they’ve got an eye towards an IPO or a sponsor-to-sponsor transaction. And then it — and its 4.5x net debt ratio — will be someone else’s problem potentially heading into a downturn. There is no coincidence here from a timing perspective. Vicious.
*****
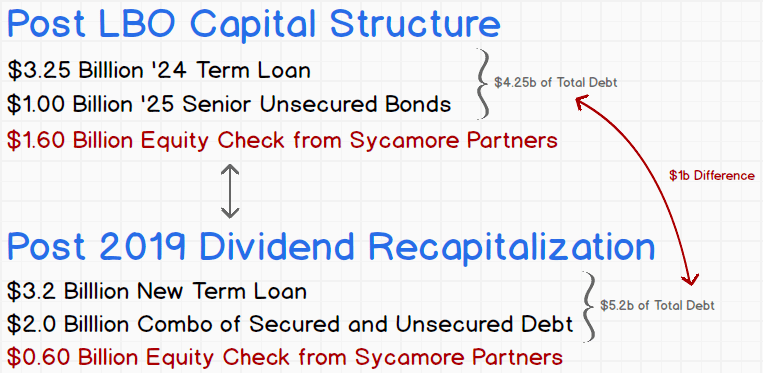
You’ll recall that Staples NAD went out to market shopping Sycamore’s scraps….uh…we mean a new $3.2b first lien term loan and a package of secured and unsecured notes to refinance its capital structure and give Sycamore one hell of a check to cash out its equity:
Well, the market reaction was…uh…interesting. Rather than issue $3.25b of senior secured term loans, the company will complete a $2.3b term loan, splitting the rest of the capital structure between secured ($2b) and unsecured notes ($1b). And the company did have to upsize the secured note piece relative to the unsecured piece. While the yield on the secured bit was mildly tighter than anticipated, the yield on the unsecured piece priced slightly wider than initially expected, indicating that the appetite for the unsecured notes was cautious — even at nearly 11% yield. Looks like certain investors didn’t buy in to the propaganda. Or Sycamore’s reputation precedes it. Either way, Sycamore reportedly took down 18% of the unsecured allotment and apparently agreed not to trade the notes for several months to help push the deal through.
That said, will Sycamore’s dividend get paid? Well, duh, of course. The market’s reaction to the issuance has no bearing on that whatsoever. Which is not to say the reaction isn’t telling — especially when the paper immediately trades lower as it did here. Short Sycamore’s scraps.
*This thread about Staples’ new logo, however, is pure comedy:
Just imagine how amped Sycamore must be to pull out all of its equity and just ride an option for the next few years.
LIKE WHAT YOU SEE? JUST WAIT TILL YOU SEE OUR PREMIUM STUFF, DISCOVER MORE FROM PETITION